原文链接 http://allanhost.com/blog/2016/08/01/Objective-C%E5%91%BD%E4%BB%A4%E8%80%85%E6%A8%A1%E5%BC%8F.html
注:以下为加速网络访问所做的原文缓存,经过重新格式化,可能存在格式方面的问题,或偶有遗漏信息,请以原文为准。
今天想和大家分享的是命令模式。下面还和之前一样,先给出基本的定义。
命令模式(Command) 将一个请求封装为一个对象,从而使你可用不同的请求对客户进行参数化;对请求排队或纪录请求日志,以及支持可撤销的操作。
那么让我们简要的说一下命令模式的特点:
- 它能比较容易地设计一个命令队列;
- 在需要的情况下,可以较容易地将命令记入日志;
- 允许接收请求的一方决定是否要否决请求;
- 可以容易地实现对请求地撤销和重做;
- 新的命令类不影响其他的类,因此增加新的命令类很容易;
- 把请求一个操作的对象与知道怎么执行一个操作的对象分隔开;
下面给出基本的类结构图。
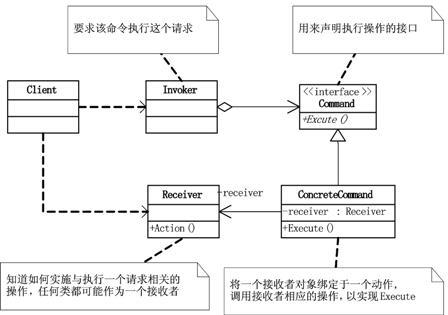
下面就根据上面的原理给出一个Demo:
Receiver类:
import
@interface Receiver:NSObject -(void)Action; @end
import "Receiver.h"
@implementation Receiver -(void)Action{ NSLog(@"执行请求!"); } @end
Commands 类:
import
@class Receiver; @interface Commands :NSObject{ Receiver myReceiver; } -(Commands)MyInit:(Receiver*)receiver; -(void)Execute; @end
import "Commands.h"
import "Receiver.h"
@implementation Commands -(Commands*)MyInit:(Receiver *)receiver{ myReceiver = receiver; return self; } -(void)Execute{ return; } @end
ConcreteCommands 类:
import "Commands.h"
@class Receiver; @interface ConcreteCommands :Commands -(ConcreteCommands*)MyInit:(Receiver*)receiver; @end
import "ConcreteCommands.h"
import "Receiver.h"
@implementation ConcreteCommands -(ConcreteCommands*)MyInit:(Receiver *)receiver{ myReceiver = receiver; return self; } -(void)Execute{ [myReceiver Action]; } @end
Invoker类:
import
@class Commands; @interface Invoker :NSObject{ Commands myCommands; } -(void)SetCommands:(Commands)commands; -(void)ExecuteCommand; @end
import "Invoker.h"
import "Commands.h"
@implementation Invoker -(void)SetCommands:(Commands *)commands{ myCommands = commands; } -(void)ExecuteCommand{ [myCommands Execute]; } @end
Main :
import
import "Receiver.h"
import "Commands.h"
import "ConcreteCommands.h"
import "Invoker.h"
int main(int argc,const char * argv[]) { @autoreleasepool{ Receiver *r = [[Receiver alloc]init]; Commands *c = [[ConcreteCommands alloc]MyInit:r]; Invoker *i = [[Invoker alloc]init]; [i SetCommands:c]; [i ExecuteCommand]; } return 0; }