原文链接 https://lingxiankong.github.io/2015-04-23-GBP.html
注:以下为加速网络访问所做的原文缓存,经过重新格式化,可能存在格式方面的问题,或偶有遗漏信息,请以原文为准。
本文对Group Base Policy(GBP)进行入门介绍。
BluePrint信息
Drafter: Kyle Mestery
Assignee: Sumit Naiksatam
Company: Cisco
GBP简介
GBP,全称Group Based Policy,基于组的策略,OpenStack提供声明策略模型,给用户提供了简单的面向应用的接口。
当前neutron抽象出的这种对应传统网络设备的模型,仅适合有网络基础的网络管理员使用与配置,对于应用管理员或应用开发者(后简称应用人员)来说,很难正确的配置一整套应用系统的网络连通性(包括安全策略)。GBP正是为了解决这一问题而生的。GBP像是在应用管理员与neutron传统模型之间增加了一个层翻译,将应用管理员的网络需求,通过neutron中传统资源的组合配置实现。GBP本身主要通过网络端点(network endpoint)组和策略(policy)组成的模型,抽象应用管理员或应用开发者所描述的网络连通性的需求。
场景介绍
下面举一个应用系统上线的示例,来描绘GBP的用途。
例如某个应用系统(如,电商平台,只是举例^_^)由三个主要的服务组成:web服务、app服务、db服务。可能一个服务分布式部署在多个VM上,那么我们叫这一组提供同样服务的VM为服务节点组,单个VM叫服务节点。那么我们姑且命名部署这三种服务的VM为web节点、app节点、db节点。那么,这套应用系统要想正常对外提供服务,在网络层面可能有如下需求:
- web节点的80、443端口允许访问
- app节点的8773端口允许web节点访问
- db节点的5432端口允许web节点、app节点访问
- 各个节点都允许ICMP协议
- 除了上述的各个允许的访问,其他访问全部拒绝
在传统neutron的模型中,我们要做到上述需求,需要为每个服务节点组创建不同的安全组,指定安全组创建各种代表应用节点网卡的port,给每个安全组配置不同的安全组规则。
但是上述的访问需求只是简单的几条,如果访问策略很多、很复杂,并且再加上防火墙,再配置防火墙规则,再加上路由器并配置策略路由,对于没有网络基础薄弱的应用管理人员或应用开发者就显得困难了,而且一旦配置错误可能影响很严重,也不利于维护。
如果我们把上述几个规则中的“允许”、“拒绝”抽象成Action,“80、443端口”抽象成Classifier,“服务节点组”抽象成Group,上述每条规则抽象成Policy Rule,整个访问策略抽象成Policy Rule Set。这样似乎就与应用人员更贴近些了。如上的抽象这就构成了GBP的基本模型。如下图所示:
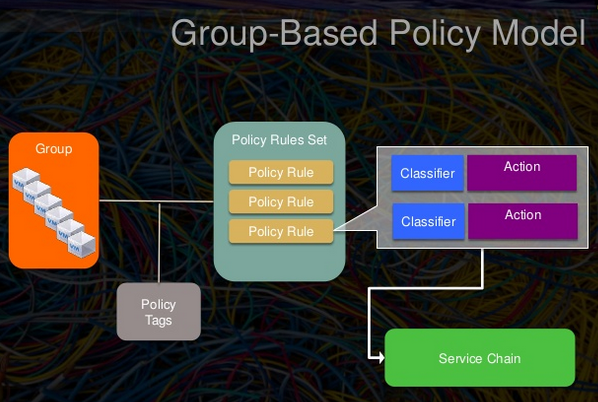
相关概念
Policy Target (PT):应用策略的最小资源,映射到neutron的一个port
Policy Target Group (PTG): PT的集合,代表一种应用服务
Policy Rule (PR):定义了两个PTG之间连通性的单个规则,每个PR由 Classifier, Action组成
Policy Rule Set (PRS): PT的集合,定义了一个PTG所代表的应用服务的访问策略,即用来定义PTG之间的访问策略
Classifier: 规则类别,如上面场景中的http协议80端口
Action: 规则的动作,如允许、拒绝
操作示例
# Create allow action that can used in several rules
gbp policy-action-create allow --action-type allow
# Create ICMP rule
gbp policy-classifier-create icmp-traffic --protocol icmp --direction bi
gbp policy-rule-create ping-policy-rule --classifier icmp-traffic --actions allow
# Create SSH Rule (Optional)
gbp policy-classifier-create ssh-traffic --protocol tcp --port-range 22 --direction bi
gbp policy-rule-create ssh-policy-rule --classifier ssh-traffic --actions allow
# Create HTTP Rule
gbp policy-classifier-create web-traffic --protocol tcp --port-range 80 --direction in
gbp policy-rule-create web-policy-rule --classifier web-traffic --actions allow
# Create HTTPs Rule
gbp policy-classifier-create secure-web-traffic --protocol tcp --port-range 443 --direction in
gbp policy-rule-create secure-web-policy-rule --classifier secure-web-traffic --actions allow
# ICMP policy-rule-set
gbp policy-rule-set-create icmp-policy-rule-set --policy-rules ping-policy-rule
# WEB policy-rule-set
gbp policy-rule-set-create web-policy-rule-set --policy-rules web-policy-rule
# Policy Target Group (PTG) creation
gbp group-create web
gbp group-create client-1
gbp group-create client-2
# Policy Target creation
WEB1=$(gbp policy-target-create web-ep-1 --policy-target-group web | awk "/port_id/ {print \$4}")
CLIENT1=$(gbp policy-target-create client-ep-1 --policy-target-group client-1 | awk "/port_id/ {print \$4}")
CLIENT2=$(gbp policy-target-create client-ep-2 --policy-target-group client-2 | awk "/port_id/ {print \$4}”)
# VMs creation
nova boot --flavor m1.nano --image cirros-0.3.2-x86_64-uec --nic port-id=$WEB1 web-vm-1
nova boot --flavor m1.nano --image cirros-0.3.2-x86_64-uec --nic port-id=$CLIENT1 client-vm-1
nova boot --flavor m1.nano --image cirros-0.3.2-x86_64-uec --nic port-id=$CLIENT2 client-vm-2
# policy-rule-set Association
gbp group-update client-1 --consumed-policy-rule-sets "icmp-policy-rule-set=true,web-policy-rule-set=true"
gbp group-update client-2 --consumed-policy-rule-sets "icmp-policy-rule-set=true,web-policy-rule-set=true"
gbp group-update web --provided-policy-rule-sets "icmp-policy-rule-set=true,web-policy-rule-set=true"
价值分析
前面Blueprint介绍时已经写出,GBP是由cisco公司主导的一个特性。GBP这套模型来自于cisco的ACI。ACI全称Application Centric Infrastructure,是cisco公司于2013年11月正式推出的一套基于硬件的SDN解决方案架构。我们可以看到GBP的模型虽然号称作为neutron现有模型的补充,但也可以作为现有模型的替换,与现有模型功能重复。有一种cisco用GBP绑架OpenStack的嫌疑。这也是为什么neutron中一部分人不同意GBP。所以虽然GBP的BP提到了neutron中并被approve,但是代码还是在stackforge,而且应该会另起炉灶。
不过,从GBP的面向应用的思路,可以启发我们,是否可以有一个这样的项目,位于neutron或各种SDN controller的上层,更贴近应用用户,翻译用户需求(包括连通需求、安全需求),就像heat做应用编排一样,编排云平台上一个应用系统的网络,让用户在云平台上能更简单的配置网络。
参考链接
https://blueprints.launchpad.net/neutron/+spec/group-based-policy-abstraction
https://wiki.openstack.org/wiki/GroupBasedPolicy
https://launchpad.net/group-based-policy
https://github.com/stackforge/group-based-policy
http://www.slideshare.net/sumit_naik/open-stack-gbp-final-sn4slideshare